Organization Chart of Local Government
Please note: This page is not intended to take the place of the
lecture and reading assignments but as a study aid. I would appreciate
hearing from you on updating any missing information or misinformation
so I can update it. I have not attempted to include every detail
but a general idea to help with remembering the information. E-mail
me at Tee with any comments.
IV. Local Government
We all live under 3 governments -- National, State, and Local.
The US has appx 87,000 governments. Most are at the local
level and include special districts.
Special Districts -- most numerous form of local govt. They are 1 function govts. that usually are created by the state legislature and governed by a board of directors. May be called authorities, boards, corporations or simply districts. Must be classified as a special district because they have the following characteristics:
A. Counties-- are to the state what the states are to the nation. An administrative arm of the state, created to serve its needs and purposes. Issue state automobile licenses, enforce state laws, registers voters, conducts elections, collects some state taxes, and helps administer justice. Also the county conducts health and welfare programs, maintains records of vital statistics (such as births and deaths), issues various licenses, collects fees, and provides a host of other public services.
Counties have no power that the state can't abolish (get rid of). Louisiana has parishes instead of counties. Rhode Island and Connecticut have counties without a government.
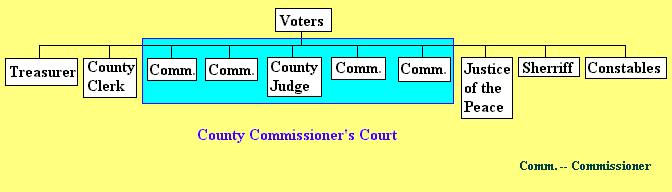
Organization Chart of Local Government

Plural Executive form of govt.
Commissioner's Court -- members include the County Judge as the chair and 4 elected commissioners. functions are administrative rather than judicial. Adopt county budgets, set tax rates, conduct elections, operate county courthouse and building maintenance as well as county jail building maintenance. Also included are build and maintain county roads and bridges, and administer county health and welfare programs.
Problems with plural executive --
Solutions to problems -- some states have proposed the creation of county commissioner's court with a county administrator.

B. Municipal Government (City) -- appx. 80% of population in Texas is from metropolitan areas. Provide services such as police, city laws, road maintenance, public services including race relations and public transportation. When you provide services you have a bureaucracy. Revenue is generated through taxes, fees, and bonds.
2 classifications of municipalities --
1. General Law City -- A city operating under general state
laws that apply to all local governmental units of a similar type.
Usually have a population of less than 5,000.
2. Home Rule City -- A city with a charter allowing local
voters to frame, adopt, and amend their own charter. Usually have
a population of more than 5,000. This allows them greater
flexibility in the structure of local govt.
4 types of City government --
Strong Mayor Council -- Dallas, San Antonio, Houston and El Paso
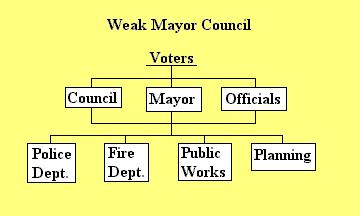
Weak Mayor Council -- Conroe
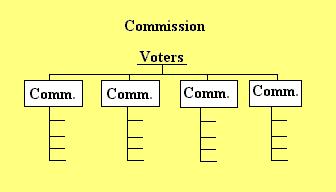
Commission -- founded in 1901 in Galveston after hurricane
Council Manager -- founded 1908 in Pennsylvania; Amarillo and
Terrell were the 1st cities in Tx with this form of govt. in 1913.
Strong Mayor Council -- the mayor has hire/fire power, preparation of budget and administration control, has veto power over the council. 8 of 10 large cities have this form except for San Antonio and Dallas.
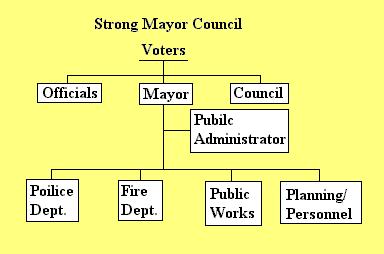
Weak Mayor Council -- the mayor shares power with the council and officials. None of the larger cities in Tx. use this because there is a lot of confusion due to no chief executive.
Commission -- least popular, each commissioner has 1 or more functional areas. No home rule city has this form. PROBLEMS: no single executive, overpay in policy making and other matters.
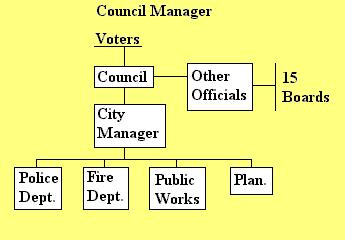
Council (Commission) Manager -- most popular structure, appx. 90% (if population is over 10,000) cities in the U.S. have this form. Has the following characteristics: City council or commission members, a city manager who can be appointed and removed by the council, elected mayor.
Pay: varies from city to city, some get nothing (volunteer basis) while others get paid by the meeting or yearly.
City Manager -- chief public administrator of the city, in charge
of all city departments and has hire/fire power over the depts.
Responsible for the budget, oversee public utilities like the water,
elec., phone, cable and etc... Also chief advisor to the city council on
city affairs.
Ex.: police chief fired by city mgr., the chief drove city
car out of town and had an accident. The police chief received a
DWI.
Pay: pay scale depends on city charter but usually well paid for the position.
Consolidation of Government
Consolidation -- The union of two or more governmental units
to form a single unit. This is easily said but difficult to do.
Ex. County and city jails. Most significant consolidation is
in Miami -- the county is a union of 26 municipalities and operated under
the home rule charter and council manager system.
Largely the state constitution disallows consolidation on a major scale.
Minor consolidation can be done.
Current Events -- Sec. Gen. of NATO - Jabier Solana, 19 countries
in NATO, continuing air strikes, hit Milosevic's headquarters again (a
23 story bldg.), deputy premier of Yugoslavia said the pres. (of Yugo.)
should stop lying to people about the country being able to handle sustained
air strikes. They would agree to an international presence but not
NATO. U.S. proceeding with calling of the reserves.
Reverend Jesse Jackson taking a group of ministers to Yugoslavia to
aid the American POW's.
North Korea -- running out of food, had been getting food from the
World Food Bank
Another gun control bill in the works since the Colorado incident at
the school
"The football" -- the guy who carries it was left at a meeting and
had to walk to the Whitehorse.
Consolidation of Government
Another form is the COG's who do not posses taxing nor lawmaking authority therefore they are not a true government.
Council of Governments -- A voluntary organization of counties
and municipalities concerned with area wide problems. They perform
regional planning activities and provide services requested by member governments
or as directed by federal and state programs. Advisory role only.
Review and comment on grant proposals and the effects on the people they
are serving.
EX. garbage automation
Where do they get their funds? From the members who join and pay their membership fees such as the cities, towns, and etc...
Policy Making by American Governments
Public Finance -- encompasses Economics (social science) and
is based on human behavior and embedded with politics.
EX. Rumors can cause the stock market to increase and/or decrease
GDP -- Gross Domestic Product; all goods and services produced
in the U.S. including those owned by other countries.
GNP -- Gross National Product; all goods and services
produced in the world by American companies.
Fiscal and Monetary Policy -- affect the national economy
Monetary Policy -- The use of changes in the amount of money in circulation to alter credit markets, employment, and the rate of inflation.
The Federal Reserve Board with Alan Greenspan (chairman) established in 1913, is an independent executive agency which meets and makes decisions about monetary policy 8 times per year. If there is an opening in the board, then the president can appoint with the approval of Congress and serve for 14 years.
Fiscal Policy -- The use of changes in government spending
or taxes to alter national economic variables, such as the rate of unemployment.
Involved the federal budget and the tax policy
The budget involves how much to spend, what to spend it on, and
how long to spend.
Tax policy concerns federal revenue and relates to taxes, and will
they go up or down.
EX. Dick Army (House Majority Leader)
proposed a flat tax rate of appx. 17%, while other have proposed a consumption
tax, or a tax on everything to replace the present income tax system.
Economic Theories
1. Classical Theory -- non-interference from the govt.
or laissez faire approach.
EX. pres. Hoover and the depression
2. Gold Standard -- 1914 - 1933; dollars were backed by
gold however, in times of crisis such as a war or depression the gold couldn't
back it up. The gold standard, guaranteed the gold value of the dollar
abroad. Freed from this, the FRB could expand the supply of currency
in circulation, thus enabling monetary policy to become a weapon for economic
recovery (Roosevelt)
3. Keynes Theory -- typically associated with the use
of fiscal policy to alter national economic variables -- for ex, increased
govt. spending during times of economic downturns.
If relief can't come from thrift of individuals or business then it
must come through the from of govt. spending in the form of public works
and/or cutting taxes. At the beginning of this time period there
was appx 25% unemployment whereas today there is about 4%. Demand
- side crisis , "prime the pump"
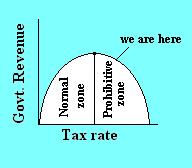
4. Supply Side Theory -- pres. Reagan's "trickle down
theory", who believed that the key to restoring corporate profits was to
cut taxes and to eliminate govt. regulation of business.
Laffer curve -- A curved graph that illustrates a relationship between tax rates and government revenues. As tax rates increase from zero, revenues increase until an optimum is reached. But if tax rates are further increased, they are supposed to discourage government spending and business investment, thereby reducing revenues.
Texas Finance -- economy stable in early '80's due to booming
oil industry and related businesses. Mid '80's oil prices fell and
unveiled many underlying problems.
Problems: Education, retraining state work force, building and
operating prison system, funding and managing entitlement (welfare) programs.
Other problems included the breakdown of Tx banking system and real estate
industries, cratering in real estate values, loss and defaults on debts.
Nat'l funding was cut and Texas depended on the state more
increase in demand for services due to changes in environment, change of attitude toward govt. Ex. public transportation, interstate and highway system, Ex of attitude: gun control and general welfare of citizens. Expanding concept of Democracy including economic changes -- wage demands to increase the minimum wage.
1. Education -- most costly state service; Involves
nat'l govt., state regulations and local ISD's. Tx schools funding
comes from a school fund and the ISD's have control over the spending based
on attendance. Junior College's funds are received in part thru local
property taxes as well as the state grants and gifts.
Permanent University Fund -- money comes
from land sales, rentals, and royalties off public lands. A.K.A.
the PUF fund. UT and A&M system which were the only 2 universities
at the time of funding creation.
2. Human Services -- 2nd largest $ funding TANF (AFDC) and includes medical services
3. Public Highways and Roads -- over 70,000 miles of highways, includes FM and park roads. Money comes from fed. govt. for interstates. $ comes from fuel and vehicle taxes.
4. Public Health Services -- provided by Dept. of MHMR (Mental Health Mental Retardation), this dept oversees water, liscensure of hospitals and nursing homes.
5. Public Safety -- DPS, TYC (Texas Youth Commission) and _______ (I didn't catch this one so if you know please let me know.)
State Revenue --
Federal grants and aid, leases of public lands,
misc. fees such as permits, and investments, taxes.
Most from Sales Tax -- chief revenue and the most significant tax
Ideal tax -- has the following characteristics
1. produces a lot of money
2. one that wouldn't have high admistration
costs
3. one that people would not object to
paying
Severance Tax -- an excise tax levied on a natural resource when that resource is severed (mined, pumped, or gathered) from the earth
Revenue Shortfall -- not enough money and
you have 4 choices
1. develop new taxes
2. increase the rate on existing taxes
3. state income tax
4. downsize or curtailment of services
Lottery money goes into the General Revenue Fund
Foreign & Defense Policy
relatesto goals the govt. wants to achieve and
the strategies to achieve these goals
military intervention, and isolation.
Foreign and Defense Policy
Foreign Policy -- A nation's external goals and the techniques and strategies used to achieve them.
Diplomacy -- The total process by which states carry on political relations with each other; settling conflicts among nations by peaceful means.
Economic Aid -- Assistance to other nations in the form of grants,
loans, or credits to buy the assisting nation's products. Technical
Aid -- The sending of experts with technical skills in agriculture,
engineering, or business to aid other nations.
Last resort under diplomacy is military intervention.
Isolationism-- Abstaining from an active role in international affairs or alliances, which characterized US foreign policy toward Europe during most of the 19th century. This policy was temporarily overthrown during W.W.I and permanently shattered by the bombing at Pearl Harbor and W.W.II.
JFK-- Said that domestic policy can hurt you but foreign policy can kill you.
Showed History Channel film on Anzio
Cold War -- The ideological, political, and economic impasse that existed between the US and the Soviet Union following W.W.II
Korean War -- civil war between the communist N and democratic S, US entered as a police action authorized by the UN, an armistice was signed with the N but as of today a treaty has not been signed. There are still flare ups in the area and the US still has appx. 30,000 troops in place.
Sputnik -- 1957 satellite launched by Soviets and was the first to circle the globe. At this time the US had intercontinental missle capabilities but when satellite launched it showed us that they also possesed intercontinenetal capabilities.
Cuban Missle Crisis -- the Soviets had decided to place offensive missiles in Cuba, the US set up a naval blockade around the island, the Soviet ships returned to Russia and we agreed not to invade Cuba and to remove some of our missiles that were near the Soviet border.
Vietnam -- began shortly after Korean conflict, the French army in Indochina wasdefeated by the communist forces of Ho Chi Minh and the country became divided, the US supported the S and "advisors" were sent to increase support, conflict escalated into a full undeclared war and over 58,000 Americans were killed
Detente -- relaxation of tensions between nations, stresses direct cooperative dealings with Cold War rivals but avoids ideological accommodation. Relaxation of tensions with the Soviets and the US and also included China
Balance of Terror
MAD -- Mutually Assured Destruction
There were a number of treaties to reduce the threat of MAD.
Strategic arms reductions, demise of communism and Soviet Union, and others
The dissolution of the Soviet Union began channeling their funds away
from the military and began Glasnost which means openness and a restructuring
of Russia.
Berlin wall came down